|
|
|
Explanations II ::
Homepage:: TRILOBITA:: Trace fossils:: Preparation:: Cabinet:: Literature:: Links:: Geological Time:: Special::
The Team :-)
Body planes:: Facial sutures:: Terminology::
|
Some explanatory References II- The next Step becoming a Trilophile - |
|
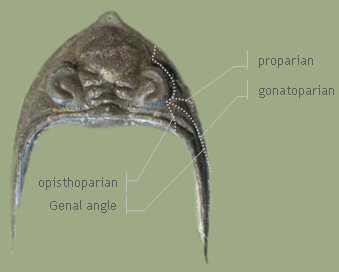
Facial suturesWith the following graphic below, our Zlichovaspis sp. demonstrates elementary facial sutures of trilobites anatomy. |
|
|
|
|
|
Cephalon, dorsal view (Zlichovaspis sp.)
|
Like mentioned before in chapter TRILOBITA, trilobites had an repeating ecdysis (moulting) during the body growth phases from larval stage to adult trilobite. During moulting process, the facial sutures (Suturae) representing the breaking points between cranidium (glabella+ fixigenae) and librigenae including conjunctive structures. The course of sutures continuing, passing over the doublure, at cephalons ventral side, cause moulting is only possible in common interaction with hypostome and rostral plate. Furthermore sutures are one of the key factors in classification of trilobites groups.
The definition of a suture is defined by it's position at cephalons edge relative to the genal angle. There are three main types of facial sutures distinguished as followed: Proparian sutures are anterior advancing the genal angle. The gonatoparian type is ending at the genal angle (travelling). Finally the opisthoparian suture are ending at the posterior cephalons edge (lagging).
These courses are described at the cephalon of our Zlichovaspis sp. (dorsal view) using the punctated lines. Of course every species has it's own one characteristic type of facial sutures. Zlichovaspis sp. has proparian sutures.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|